Design and engineering of tumor-targeted, dual-acting cytotoxic nanoparticles
In the frame of the collaboration of three units of NANBIOSIS, researchers of CIBER-BBN Groups proposed a strategy to simultaneously deliver anticancer drug pairs, composed by a tumor-targeted protein nanoparticle and an antiproliferative drug, with specific activ-ity for the same type of cancer.
These three units are:
- NANBIOSIS U1 Protein Production Platform (PPP), at IBB-UAB, led by Toni Villaverde y Neus Ferrer
- NANBIOSIS U18 of Nanotoxicology Unit, at Institut de Recerca. Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau, led by Ramón Manques and Isolda Casanova, and
- NANBIOSIS U29 Oligonucleotide Synthesis Platform (OSP) at IQAC_CSIC, led by Ramón Eritja and Anna Aviñò
The results on the investigation have been published in an article entitled “Design and engineering of tumor-targeted, dual-acting cytotoxic nanoparticles”· by Acta Biomaterialia
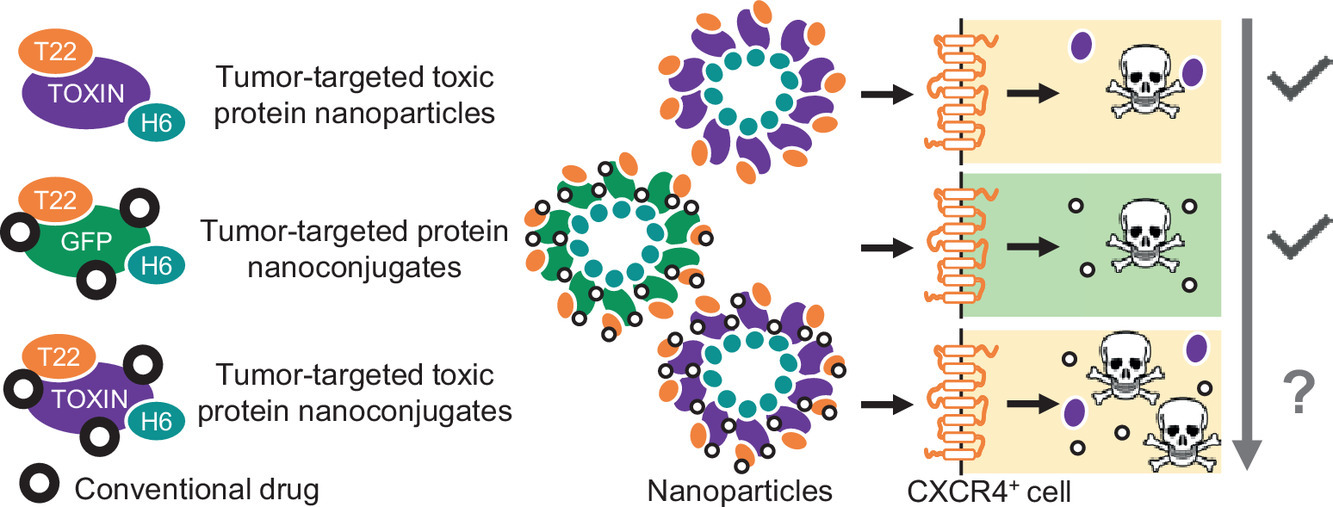
The researchers have explored the possibility to conjugate tumor-targeted cytotoxic nanoparticles and conventional antitumoral drugs in single pharmacological entities using CXCR4-targeted self-assembling protein nanoparticles based on two potent microbial toxins, the exotoxin A from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the diphtheria toxin from Corynebacterium diphtheriae, to which oligo-floxuridine and monomethyl auristatin E respec- tively have been chemically coupled.
The resulting multifunctional hybrid nanoconjugates, with a hydro- dynamic size of around 50 nm, are stable and internalize target cells with a biological impact. Although the chemical conjugation minimizes the cytotoxic activity of the protein partner in the complexes, the concept of drug combination proposed is fully feasible and highly promising when considering multiple drug treatments aimed to higher effectiveness or when facing the therapy of cancers with acquired resistance to classical drugs.
Thus, these results open a wide spectrum of opportunities in nanomedical oncology.
Article of reference:
Eric Voltà-Durán, Naroa Serna, Laura Sánchez-García, Anna Aviñó, Julieta M. Sánchez, Hèctor López-Laguna, Olivia Cano Garrido, Isolda Casanova, Ramón Mangues, Ramon Eritja, Esther Vázquez, Antonio Villaverde, Ugutz Unzueta Design and engineering of tumor-targeted, dual-acting cytotoxic nanoparticles. Acta Biomaterialia, Volume 119, 1 January 2021, Pages 312-322), 57746-57756 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.11.018