U9-E08. Portable Tándem NanoScan SMPS Nanoparticle Sizer 3910 and Optical Particle Sizer (OPS) 3330
Equipment funded by European Union (NextGeneratioEU) -Plan de Transfomación y Resilencia


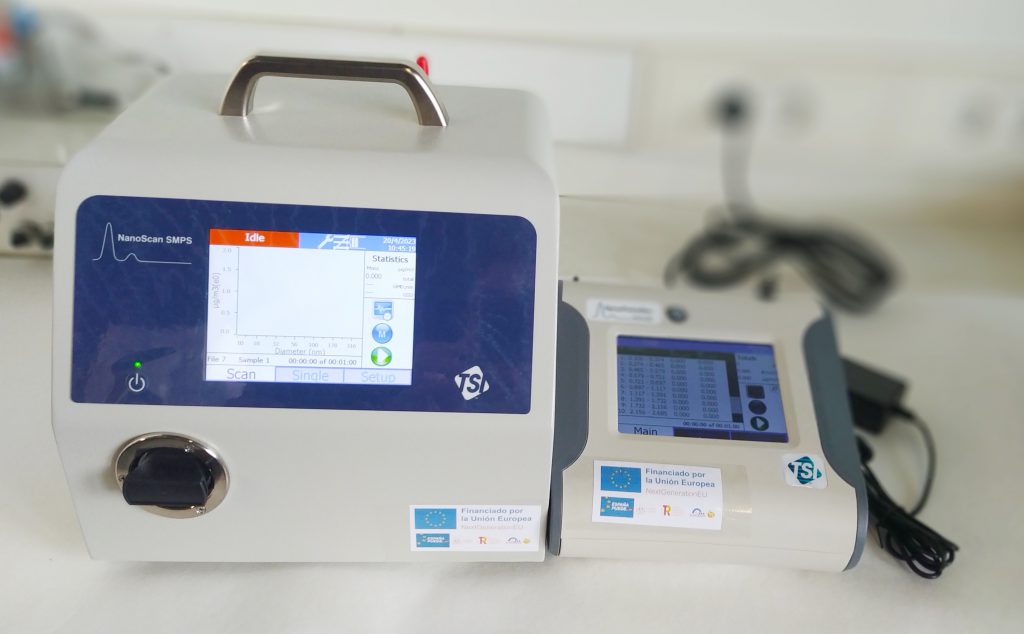
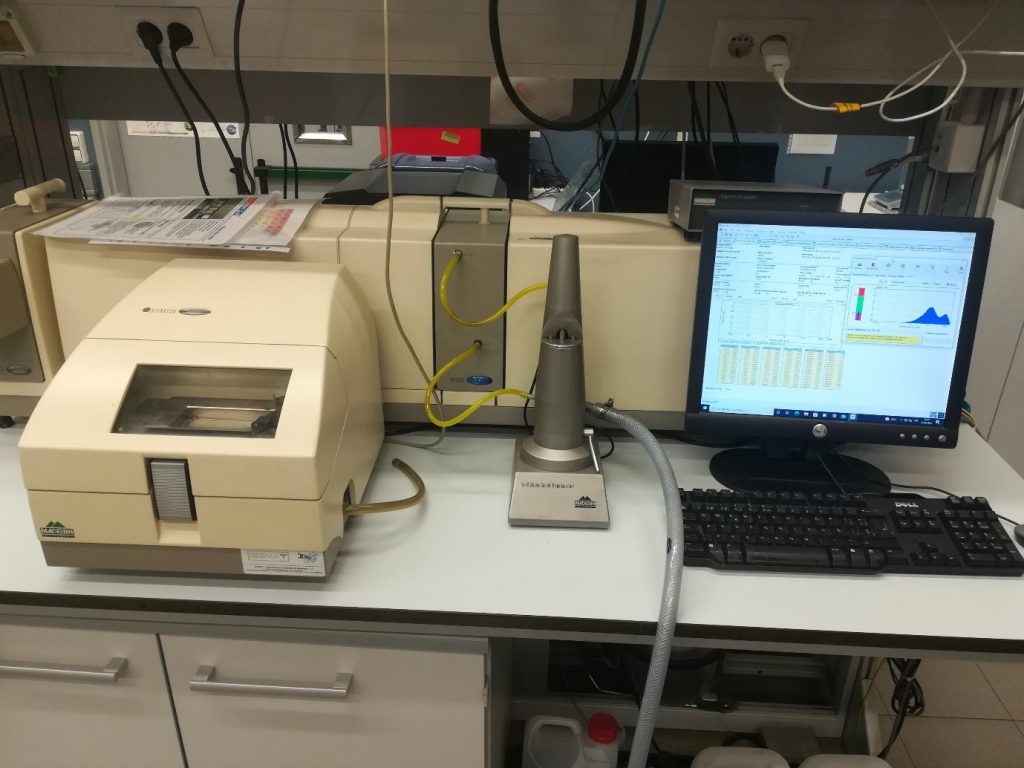
Description: NanoScan SMPS™ Nanoparticle Sizer delivers a TSI Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer (SMPS™) spectrometer in a portable package that is about the size of a basketball. Easy to use, lightweight and battery-powered, the NanoScan SMPS™ spectrometer enables investigators to collect valuable nanoparticle size data. The NanoScan SMPS™ Nanoparticle Sizer spectrometer is suitable for a variety of applications, such as a multitude of mobile studies, workplace exposure monitoring, point source identification, and student lab education. Derived from TSI core technologies, the NanoScan SMPS spectrometer is an innovative, cost effective solution for real-time nanoparticle size measurements.
Technical Specifications: Weighing less than 20 pounds (including two hot-swappable batteries), the NanoScan SMPS™ Nanoparticle Sizer 3910 measures nanoparticle size distributions from 10 to 420 nm in one minute. Its internal Condensation Particle Counter (CPC) uses isopropyl alcohol as a working fluid, so the NanoScan is suitable for use in a variety of sensitive environments. Single particle mode allows the user to monitor particle concentrations of a single, user-set particle size. Data logging is built in to the instrument, so measurements may be made without the use of a laptop.
As a package, i.e. the model 3910 combined with the Optical Particle Sizer (OPS) 3330 enables users to measure three orders of size magnitude from 10 nm to 10 µm. These instruments are affordable, portable, and provide real-time data that can be merged with the multi-instrument manager (MIM) software. Used already for cabin measurements in cars and airplanes, the sky is literally the limit when it comes to new applications. Quantification thresholds reach to maximum concentrations of up to 150.000 particles per cm3.
Applications: General applied research; Indoor/outdoor air quality investigations; Nanotechnology/nanoparticle applications; Combustion/emission research; Mobile studies; Health effects/inhalation toxicology; Occupational hygiene/workplace exposure monitoring; Point source identification.