U26-S06. Biomedical and metabolomic imaging
Biomedical and metabolomic imaging
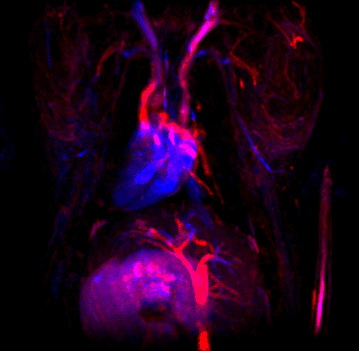
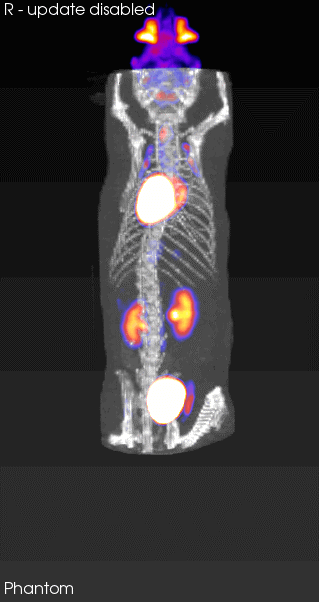
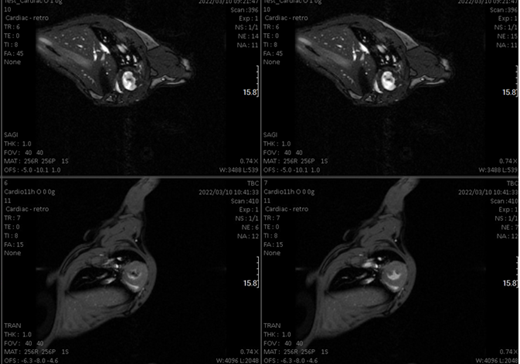
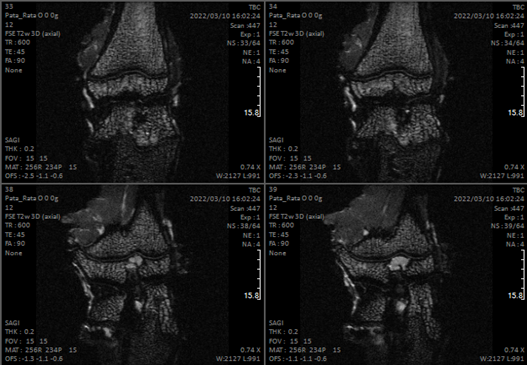
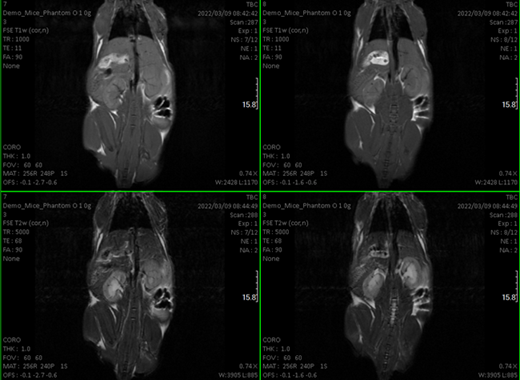
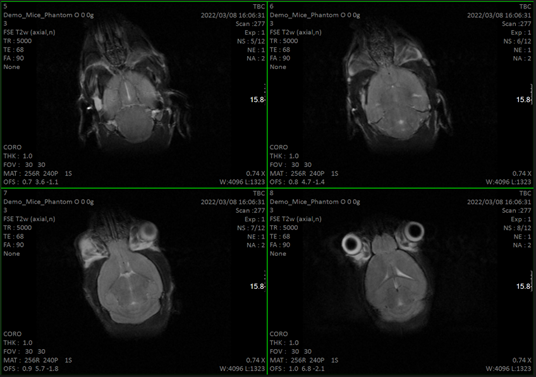
The service is intended for obtaining images animals such as mice and rats. Longitudinal studies can be performed as well. Thanks to a pre-clinical 7 T nmr equipment equipped with a PET plug-in. Co-localized NMR-PET-CT imagens can be obtained.
Customer benefits
The service is integrated in the University of Valencia core facility that ensures the correct maintenance and the offsite service runed by technicians under ISO 9001.
Target customer
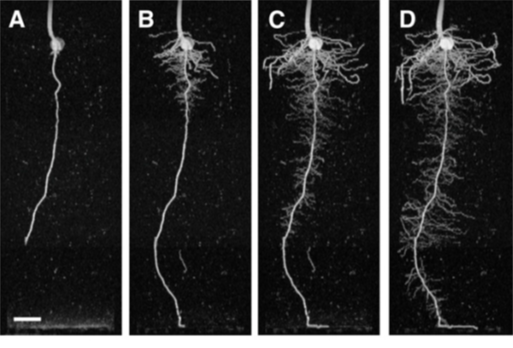
The primary audience are pre-clinic research groups that require punctual or longitudinal studies on such animals. Plant and food researchers can benefit from the fact that the equipment can acquire the image in vertical position preserving the natural flux of fluids in plants.
Additional information