Ready your proposals: Our Open Call starts on june
NANBIOSIS opens in June the 2nd Competitive Open Call of 2025 for our “Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions” and services.
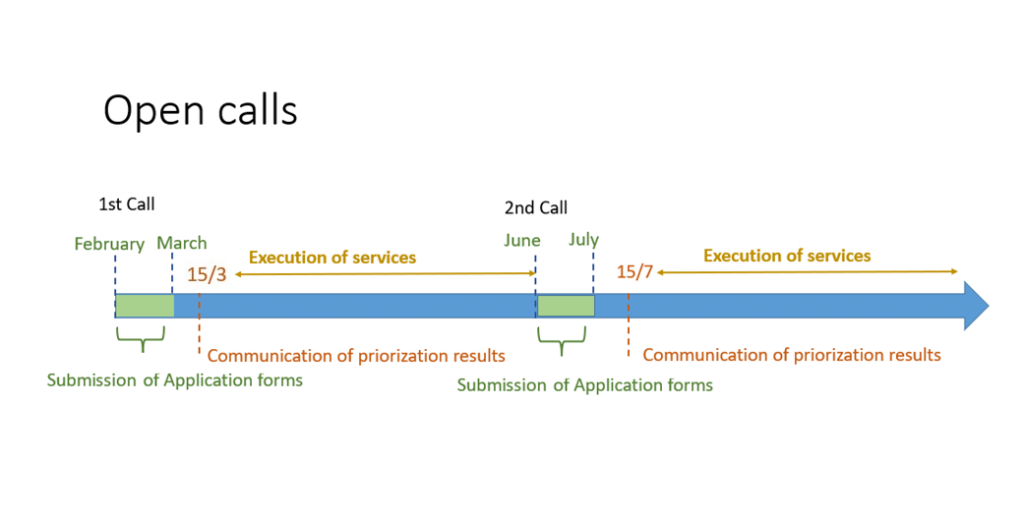
Last January, as a belated Christmas present, we opened our 1st Open Call of 2025, and it was about time to introduce you to the second call in June: offering you our discounts and preferential access during the entire month of June!
Our publicly funded facilities and internationally renowned scientist will help you design and test biomedical solutions to your heart’s content. We are open to all interested national and international users who may come either from the public or the private sector. You can apply to use our services in two modalities: under the “Competitive Open Access” (within our two designated calls) or by “Access on Demand”, your choice.
To make that happen, at least 20% of the capacity of the Units of NANBIOSIS is offered on the Competitive Open Access modality. The proposals granted under this modality will be prioritized according to criteria of scientific and technical quality and singularity. In addition, a 5% discount will be applied for those proposals that resort to at least one of our integrated services, the Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions.
NANBIOSIS is a research infrastructure for Biomedicine included in the the Spanish Map of ICTS (Spanish for “Scientific and Technical Unique Infrastructures”), approved by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades.
There are 2 calls per year for Competitive Open Access that allow the prioritization of the best proposals. Click here to apply.
As stated, the next call will open on June 2025. The applications can be submitted throughout the whole month (due date June 30th). Access application forms submitted after that date will be processed under the “Access on Demand” modality.
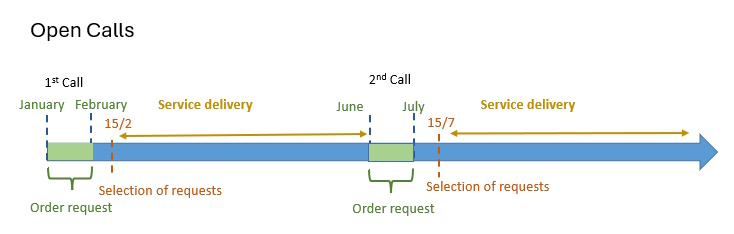
Proposals granted in the Competitive Open Access modality must meet, at least, one of the circumstances listed in the access application form (“order request“), in order to demonstrate their scientific and technical quality or singularity.
Thus, for example, applications related to R&D projects funded through national or European calls are eligible. In addition, the proposals are required to use one of the NANBIOSIS “Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions”. That implies the interaction of at least two of our Units. The choice of said Units can be modified to your specific needs.

Mark your calendar and ready your proposals! The Call will be open until the end of June 2025.
What is NANBIOSIS?
The goal of NANBIOSIS is to provide comprehensive and integrated advanced solutions for companies and research institutions in biomedical applications. All of this is done through a single-entry point, involving the design and production of biomaterials, nanomaterials, and their nanoconjugates. This includes their characterization from physical-chemical, functional, toxicological, and biological perspectives (preclinical validation).
In order to access our Cutting-Edge Biomedical Solutions with priority access, enter our Competitive Call here.
NANBIOSIS has worked with pharmaceutical companies of all sizes in the areas of drug delivery, biomaterials and regenerative medicine. Here are a few of them: