NANBIOSIS renews its accreditation as Singular Scientific and Technical Infrastructure (ICTS)
The Minister of Science and Innovation, Diana Morant, chaired the XI meeting of the Council for Scientific, Technological and Innovation Policy, in which the update of the Map of Singular Scientific and Technical Infrastructures, the ICTS Map for 2021-2024, was approved.
The ICTS are facilities dedicated to cutting-edge research of the highest quality, as well as to the transmission, exchange and preservation of knowledge, technology transfer and the promotion of innovation.
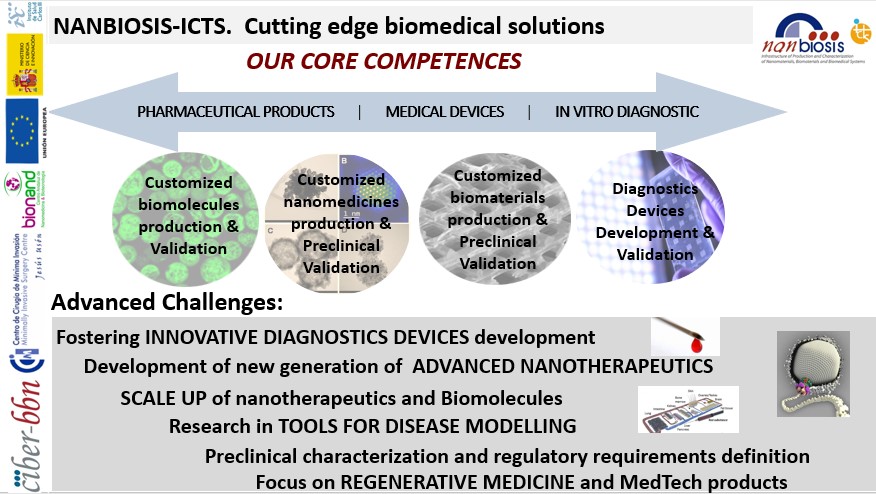
The map has 29 ICTS distributed among all the territories, includes NANBIOSIS, the Infraestructure for Production and Characterization of Nanomaterials, Biomaterials and Systems in Nanomedicine with its 26 units.
As a novelty, the update incorporates four new nodes or infrastructures associated with the ICTS. Specifically, the NASERTIC computing node in Navarra, the CIEMAT computing node in Extremadura and Madrid, and the Port d’Informació Científica data node in Catalonia are incorporated into the ICTS Red Española de Supercomputación, while the Center for Microanalysis of Materials is associated as a node to the new distributed Infrastructure of Applications Based on Accelerators. Likewise, Navarra incorporates an infrastructure to this map for the first time, an instrument that improves the management of ICTS and helps these organizations to access funding from the Ministry as well as regional and European funds, particularly the ERDF funds and the Recovery Funds and Resilience (MRR).
In this sense, the minister announced that the next call to strengthen the ICTS, scheduled for the first half of 2022, will allocate 38 million euros until 2025 to finance lines of investment associated with the construction, development, instrumentation, equipment and improvement of its scientific- techniques. The previous call, published in 2021, dedicated nearly 37 million euros to these infrastructures.
NANBIOSIS is one of the five ICTS in the area of health sciences and biotechnology. This thematic area has significantly increased its representation in the current ICTS Map. Under the concept of distributed ICTS, infrastructure networks have been established in the field of imaging, nanotechnology and omics sciences. In addition, the high biological safety laboratories are also reinforced, expanding the infrastructures of this type that offer their services.