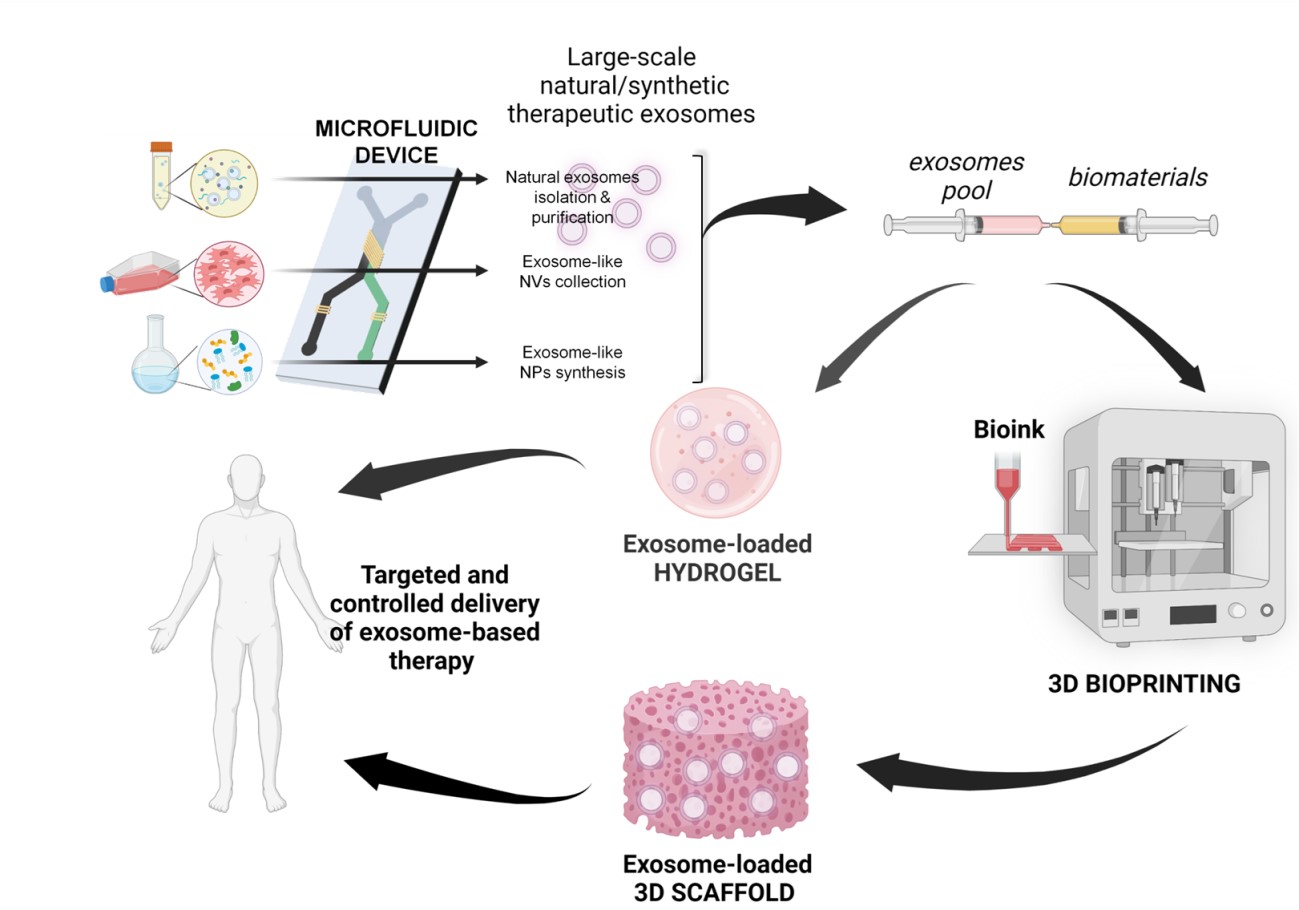
The role of microfluidics and 3D-bioprinting in the future of exosome therapy. A high impact review
Researchers of the NanoBioCel research group of the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) and CIBER BBN, belonging to NANBIOSIS U10 Drug Formulation, Bioaraba, and CONICET Foundation of Argentina, have collaborated in a studio entitled: “The role of microfluidics and 3D-bioprinting in the future of the exosome therapy” which has been published in the journal Trends in Biotechnology, whose editorial seeks particularly relevant articles.
The importance of this publication lies in the novelty and potential of nanovesicles as new therapeutic agents and the versatility of microfluidic technology in combination with 3D bioprinting to bring nanovesicles closer to the clinic.
Article of reference:
Mikele Amondarain, Idoia Gallego, Gustavo Puras, Laura Saenz-del-Burgo, Carlos Luzzani, José Luis Pedraz, “The role of microfluidics and 3D-bioprinting in the future of exosome therapy”, Trends in Biotechnology,
2023, ISSN 0167-7799
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2023.05.006.