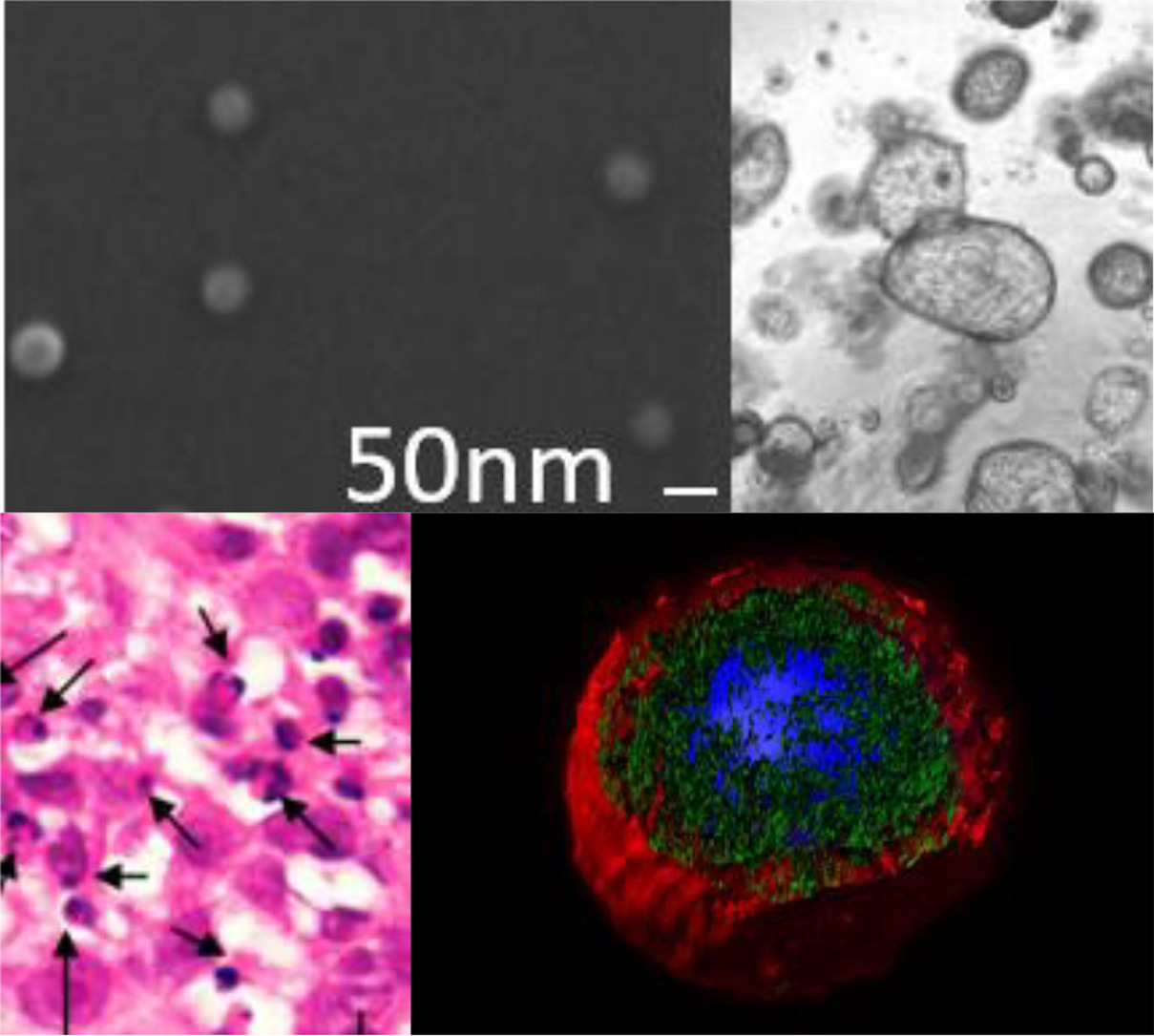
Identification of a novel nanotherapy active in cancer cells resistant to chemotherapy
Researchers of the Nanotoxicology Unit (u18-nanotoxicology-unit) led by Ramon Mangues and Isolda Casanova at the Research Institute of the Hospital de Sant Pau and the Protein Production Platform (u1-protein-production-platform-ppp), led by Antonio Villaverde and Neus Ferrer Miralles of the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, both belonging to the ICTS NANBIOSIS (nanbiosis.es) of the CIBER-BBN, have participated in the production of a novel Nanotoxin capable of selectively killing cancer cells which became resistant to chemotherapy. Development of cancer resistance frequently associates with the overexpression of the CXCR4 receptor.
It is known that chemotherapy kills cancer cells, mainly, by induction of apoptosis, after damaging the cell DNA; therefore, to survive resistant cancer cells develop anti-apoptotic mechanisms. In contrast, a Nanotoxin that has incorporated the exotoxin of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and a targeted ligand that selectively internalizes in CXCR4+ cancer cells, exploits a mechanism of cell death alternative to apoptosis, thus, effectively killing resistant cancer cells in a colorectal cancer model. The new mechanism is the induction of a blockade of protein translation, by inhibition of the elongation factor 2, which renders sensitive to therapy cancer cells resistant to chemotherapy.
The described work opens a new avenue for the exploration of antitumor activity in cancer that relapses after current therapy, an unmet medical need in oncology, and therefore, it could have an important impact in cancer patient well being.
Reference:
Naroa Serna, Patricia Álamo, Prashanthi Ramesh, Daria Vinokurova, Laura Sánchez-García, Ugutz Unzueta, Alberto Gallardo, María Virtudes Céspedes, Esther Vázquez, Antonio Villaverde, Ramón Mangues, Jan Paul Medema. Nanostructured toxins for the selective destruction of drug-resistant human CXCR4 + colorectal cancer stem cells. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.01.019.