A more effective nanomedicine has been developed for the treatment of Fabry rare disease.
28 February: International Rare Disease Day
- This is one of the major achievements of the European Smart4Fabry project, which is now coming to an end after four years of work.
- The results have been made possible by nanotechnology and the approach developed could be applied to other drugs in the future.
- The new drug improves on current treatments and helps reduce costs and improve patients’ quality of life.
Barcelona, 26 February 2021.- The advance of nanomedicine opens up new possibilities in the development of drugs, such as the one recently developed for the rare disease Fabry, with improved efficacy compared to existing authorised treatments.
Thus, the European Smart4Fabry project has come to an end with one of the best results possible: the designation of a new orphan drug by the European Commission and the possibility of making progress in the treatment of Fabry, a rare disease that is estimated to affect approximately 2.6 out of every 10,000 people in the EU.
It is a chronic debilitating disease due to recurrent episodes of severe pain that is difficult to control with conventional analgesics, and it is life-threatening due to renal failure and associated cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications.
“With this designation we have made a major achievement, not only for Fabry patients, but also for other pathologies that can benefit from this same approach, made possible by nanotechnology,” explained Nora Ventosa, Scientific Director of NANBIOSIS Unit 6 Biomaterial Processing and Nanostructuring Unit of CIBER-BBN and ICMAB-CSIC who coordinated the project.
Need for new treatments for the disease
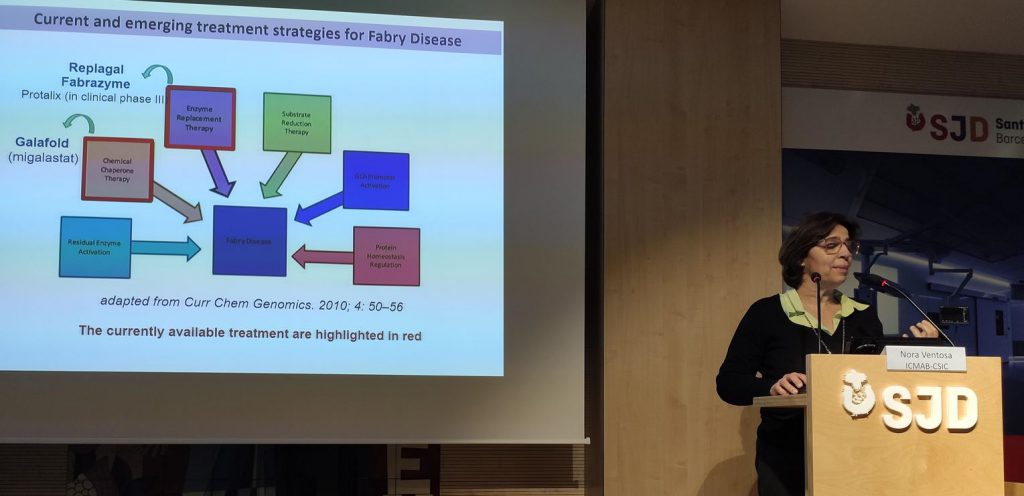
This disease, also known as Anderson-Fabry disease, represents the most common lysosomal storage disorder. It is caused by an absence or deficiency of the enzyme α-galactosidase A (GLA), which results in the lysosomal accumulation of globotriaosylceramide (Gb3) and its derivatives in the lysosomes of a wide variety of tissues, responsible for the clinical manifestations. Current treatments consist of intravenous administration of the GLA enzyme, but have limited efficacy and poor biodistribution.
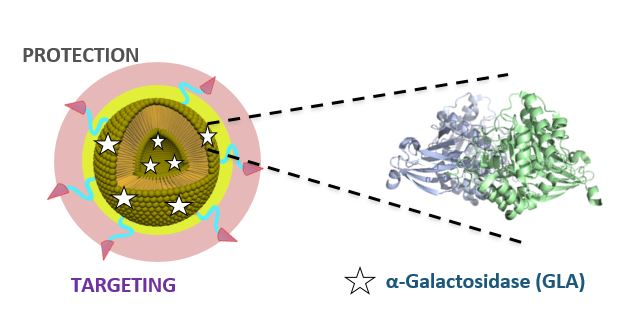
The drug that has been developed is a new nanoformulation of GLA (nanoGLA) that improves efficacy compared to the reference treatment with non-nanoformulated GLA. “The third-generation liposomal product we have developed in the project has demonstrated, at preclinical level, improved efficacy, compared to authorised enzyme replacement treatments, demonstrating that the strategy of supplying the affected cells with the GLA enzyme via the smart nanoliposome is highly successful”, explained Ibane Abasolo, Scientific Coordinator of NANBIOSIS U20 of CIBER-BBN and VHIR, who is responsible for the efficacy studies in the project.
The nanoGLA product was obtained using DELOSTM formulation technology, an innovative platform for the robust production of nanomedicines in an efficient and sustainable manner.
The Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products, the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) committee responsible for recommending orphan designation of medicines for rare diseases, has considered these results to have a clinically relevant advantage over current enzyme replacement therapies.
The designation of orphan drug, in addition to recognising the significant benefit of the new nanomedicine over products already licensed for Fabry disease, has important implications for the translation of the new therapeutic product from bench to bedside.
Those responsible for these results, including several CIBER-BBN groups, highlight that the new formulation helps to improve treatments, reduce costs, and improve the quality of life of Fabry patients.
Interdisciplinarity and public-private collaboration
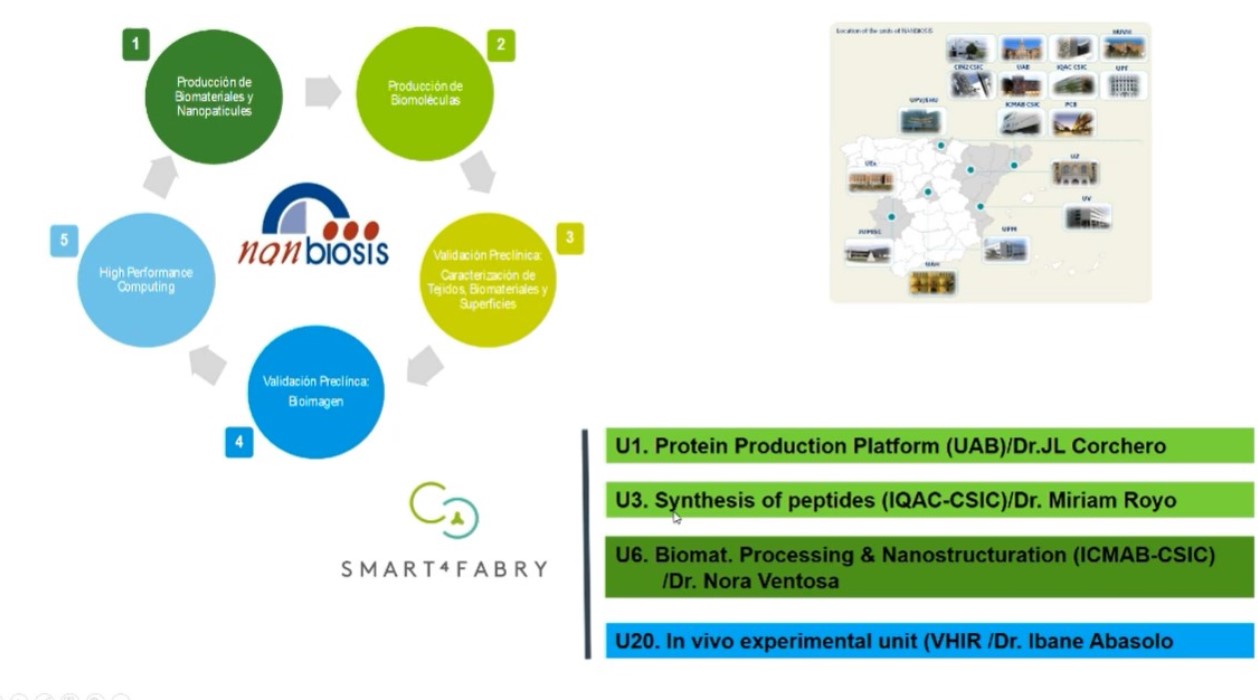
The Smart4Fabry project has been running since 2017 thanks to European funding of €5.8 million, from the Horizon 2020 programme. This was possible thanks to the collaboration of several CIBER-BBN groups and NANBIOSIS Units at the Institute of Materials Science of Barcelona (ICMAB-CSIC) with the abouve mentioned NANBIOSIS Unit 6, the Institute for Advanced Chemistry of Catalonia (IQAC-CSIC) with NANBIOSIS Unit 3 of
Synthesis of Peptides Unit, led by Miriam Royo, the Vall d’Hebron Research Institute (VHIR) with NANBIOSIS Unit 20 and the Institute of Biotechnology and Biomedicine of the Autonomous University of Barcelona (IBB-UAB) with NANBIOSIS Unit 1 Protein Production Platform (PPP), whose work in this project was led by José Luis Corchero. It has also been necessary to contribute knowledge from different academic and business disciplines.
The project consortium also includes public institutions such as the University of Aarhus (Denmark), Technion Israel Institute of Technology (Israel) and Joanneum Research (Austria); and the companies Biokeralty (Spain); Nanomol Technologies SL (Spain); BioNanoNet (Austria), Drug Development and Regulation SL (Spain), the Covance Laboratories LTD group (UK) and Leanbio SL (Spain), which have provided the necessary expertise in nanotechnology and biotechnology, physicochemical characterisation, in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation, formulation and grading of nanomedicines, and pharmaceutical development and production under the guidelines of regulatory agencies.
CIBER and CSIC, promoters of orphan drugs
Orphan Drug Designations (ODDs) seeks to facilitate the arrival of treatments for rare diseases on the market. Several incentives are associated with ODDs, such as market exclusivity, fee reductions and specific scientific advice.
To date, CIBER has promoted eleven orphan drugs designated by the EMA, mainly from the thematic area of Rare Diseases (CIBERER), this being the first from CIBER-BBN.
On the other hand, this is the fourth ODD that the CSIC has obtained, and the first time it refers to a nanoformulated drug.
Orphan drug designation by the European Medicines Agency has several advantages, such as receiving a commercialisation authorisation for 10 years during which similar products cannot be commercialised, the availability of free or low-cost scientific advice and support protocols, and exemption from designation fees. In addition, entities developing orphan drugs have access to specific grants from the European Union and member states’ programmes.
More information
Scientific Culture Unit UCC+i CIBER cultura.cientifica@ciberisciii.es
Other related news