A new nanoconjugate blocks acute myeloid leukemia tumor cells without harming healthy ones
Researchers from NANBIOSIS U18 Nanotoxicology Unit at the Institut d’Investigació Biomèdica de Sant Pau (IIB Sant Pau) and NANBIOSIS U1 Protein Production Platform (PPP) at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) toghether with researchers of Institut de Recerca contra la Leucèmia Josep Carreras (IJC) have demonstrated the efficacy of a new nanoconjugate, designed in house, that blocks dissemination of leukemic cells in animal models of acute myeloid leukemia. These results have been published in a high impact scientific journal in the field of oncology and hematology, Journal of Hematology and Oncology. Most of the experimental work has been performed in the nanotoxicology and protein production ICTS “NANBIOSIS” platforms from CIBER-BBN.
NANBIOSIS U1 PPP has advised and helped the researchers in the production of recombinant proteins, which has allowed to successfully explore the capacity of proteins from the human microbiome, that is, from bacteria and their bacteriogages, to generate, through genetic engineering, biocompatible nanomaterials and Non-immunogenic for potential use in human clinics, such as vehicles for drug delivery or regenerative medicine.
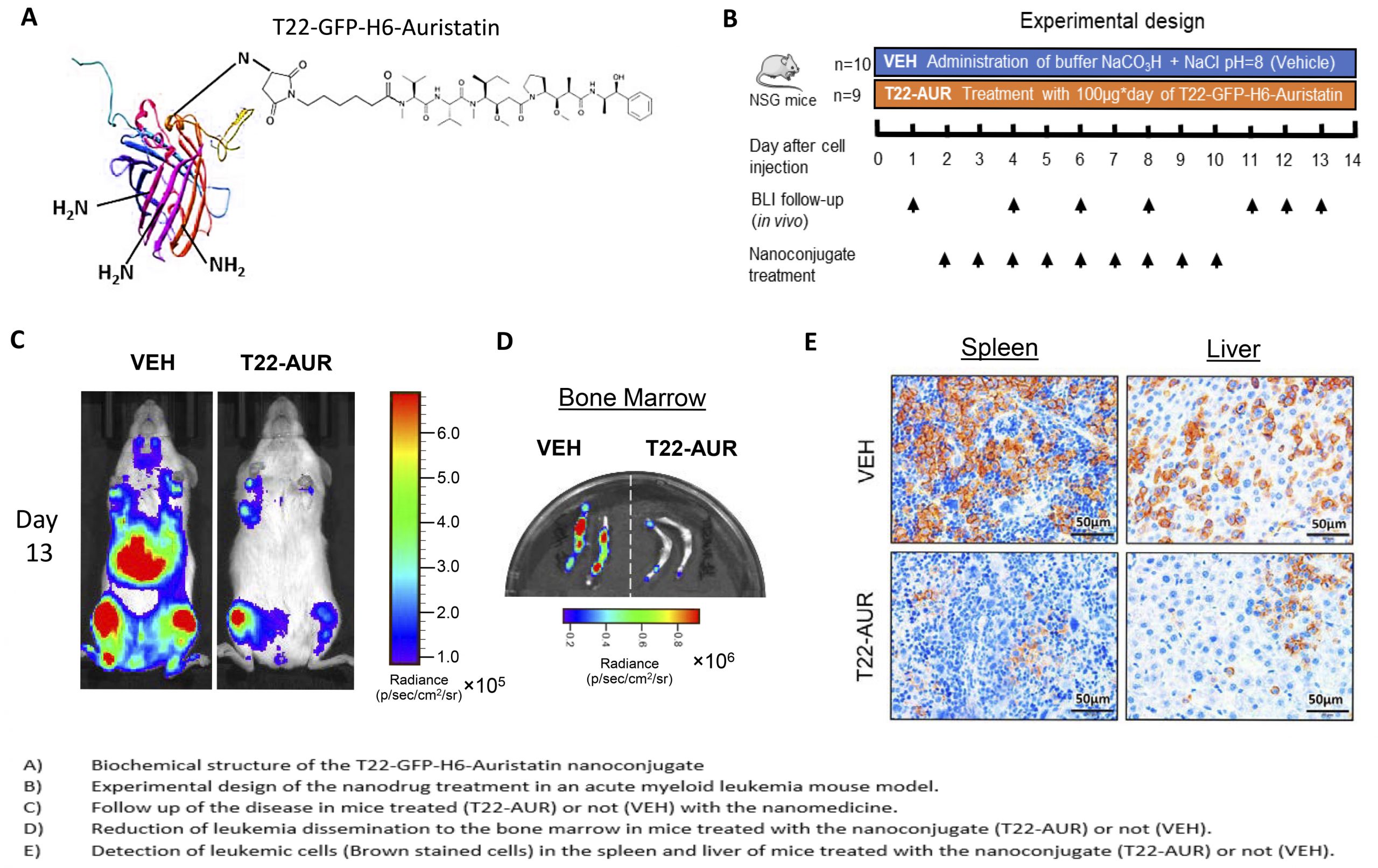
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneous disease which usual treatment is very aggressive and produces severe side effects to the patients. In order to reduce these adverse effects, the researchers have developed a nanomedicine that is specifically targeted to the tumor cells without damaging normal cells. This new protein nanoparticle is bound to a toxin, named Auristatin, which is between 10 and 100 times more potent than the drugs typically used in the clinic. In particular, this nanoconjugate is targeted only to the cells that express in their membrane a receptor called CXCR4, which is overexpressed in leukemic cells. Thus, this nanoparticle can only enter and deliver the toxin into the cells that express this receptor. It should be noted that CXCR4 is overexpressed in a large proportion of leukemic cells in patients with poor prognostic or refractory disease, so it could have a major clinical impact on these AML patients.
The researcher team led by Ramon Mangues, from IIB Sant Pau, Antonio Villaverde and Esther Vázquez, from UAB, all members of CIBER-BBN, has demonstrated that the nanoconjugate is able to internalize in the leukemic cells through the CXCR4 receptor and kill them. In addition, they have demonstrated the capacity of this nanoparticle to block dissemination of leukemic cells in a mouse model producing without any kind of associated toxicity or adverse effects. Thanks to its targeting to leukemic cells it could help AML patients that cannot be treated with current drugs because of their high toxicity, such as this experienced by elderly patients or patients with other non-favorable characteristics that exclude conventional treatment. Furthermore, the novel nanoparticle could be used to treat patients that have developed resistance to drugs or those that have experienced relapse, since their leukemic cells would likely have high expression of the CXCR4 receptor. Hence, there is a wide range of patients that could benefit of this new treatment, which could have a major clinical impact if its effectiveness was confirmed in further clinical trials.
It is worth pointing out that the CXCR4 receptor is overexpressed in more than 20 different cancer types, which expression associates with poor prognosis. Therefore, this nanodrug could be evaluated in the near future as a possible treatment in other tumor types of high prevalence.
The intellectual property of this nanomedicine has been licensed to the SME biotech Nanoligent, which aim is continuing the so far successful access to public and private funds to complete the preclinical development to enter clinical trials in acute myeloid leukemia, before being tested in other cancer types.
Article of reference:
An Auristatin Nanoconjugate Targeting CXCR4+ Leukemic Cells Blocks Acute Myeloid Leukemia Dissemination. Victor Pallarès, Ugutz Unzueta, Aïda Falgàs, Laura Sánchez-García, Naroa Serna, Alberto Gallardo, Gordon A Morris, Lorena Alba-Castellón, Patricia Álamo, Jorge Sierra, Antonio Villaverde, Esther Vázquez, Isolda Casanova, Ramon Mangues. DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00863-9