New results evidence new biomarkers for early diagnosis of P. aeruginosa infections
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common multidrug-resistant pathogen that causes acute and chronic infections. However, P. aeruginosa, as many other bacterial species, has developed resistance to antibiotics being difficult to treat. For this reason diagnostic methods allowing detection at early stages of the infection are required and, therefore, efficient biomarkers of infection are very helpful. These fast diagnosis will help on the subsequent therapeutic treatment.
The Nb4D group of CIBER-BBN and IQAC-CSIC (led by M.-Pilar Marco) has recently conducted a research to develop a highly sensitive, specific and reliable immunochemical assay to detect pyocyanin (PYO), one of the most important virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The assay uses a high-affinity monoclonal antibody produced by the unit 2 of the ICTS NANBIOSIS Custom Antibody Service (CAbS) (Dr. Núria Pascual).
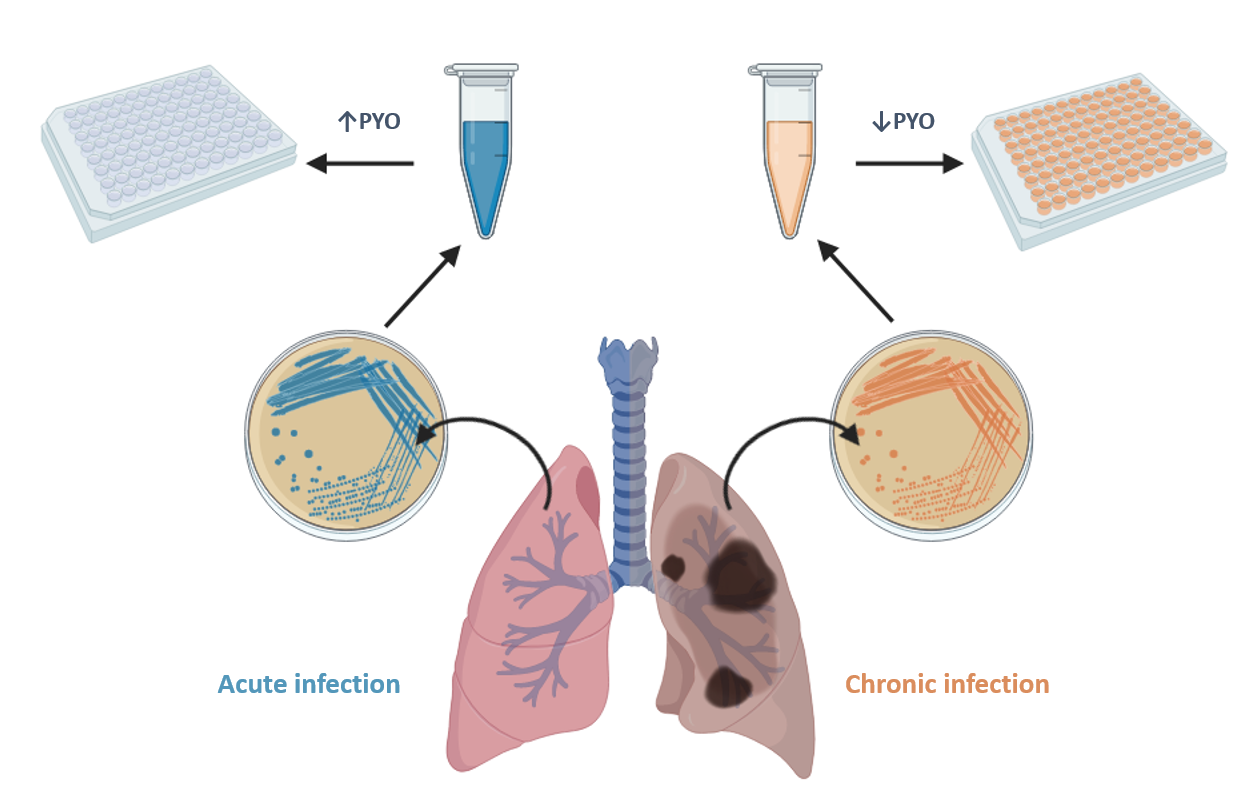
The microplate-based ELISA developed is able to achieve a limit of detection (LoD) of 0.07 nM, which is much lower than the concentrations reported to be found in clinical samples (130 µM in sputa and 2.8 µM in ear secretions). The ELISA has allowed the investigation of the release kinetics of PYO and 1-OHphz (the main metabolite of PYO) of clinical isolates from P. aeruginosa-infected patients. Significant differences have been found between clinical isolates obtained from patients suffering an acute or a chronic infection (~6,000 nM vs. ~8 nM of PYO content, respectively).
The results found point to a real potential of PYO as a biomarker of P. aeruginosa infection and the possibility to use such virulence factor also as a biomarker for patient stratification and for an effective management of these kinds of infections.
Article of referece:
Rodriguez-Urretavizcaya, B., Pascual, N., Pastells, C., Martin-Gomez, M.-T., Vilaplana, Ll.*, Marco. M.-P. (2021). “Diagnosis and Stratification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infected Patients by Immunochemical Quantitative Determination of Pyocyanin From Clinical Bacterial Isolates.” Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 11(1215). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104793