Modulation of intercolumnar synchronization by endogenous electric fields in cerebral cortex with neuroprobes by NANBIOSIS unit 8
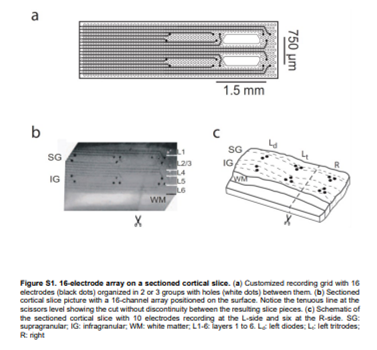
The collaboration of NANBIOSIS U8 Micro–Nano Technology Unit of the CIBER in Bioengineering, Biomaterials & Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN) at the IMB-CNM in the research carried out by scientist of Institut d’Investigacions Biomèdiques August Pi i Sunyer (IDIBAPS), Université Paris-Saclay, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) and ICREA has bien acknowledged in the publication of the results by Science Advances. Rosa Villa and Xavi Illa have been in charge of the fabrication of the probes used, more specifically, neuroprobes were designed and manufactured with 16 Ti / Au microelectrodes (20 / 200nm) on flexible polyimide substrates with open areas to improve neuronal tissue viability according to specifications.
Abstract
Neurons synaptically interacting in a conductive medium generate extracellular endogenous electric fields (EFs) that reciprocally affect membrane potential. Exogenous EFs modulate neuronal activity, and their clinical applications are being profusely explored. However, whether endogenous EFs contribute to network synchronization remains unclear. We analyzed spontaneously generated slow-wave activity in the cerebral cortex network in vitro, which allowed us to distinguish synaptic from nonsynaptic mechanisms of activity propagation and synchronization. Slow oscillations generated EFs that propagated independently of synaptic transmission. We demonstrate that cortical oscillations modulate spontaneous rhythmic activity of neighboring synaptically disconnected cortical columns if layers are aligned. We provide experimental evidence that these EF-mediated effects are compatible with electric dipoles. With a model of interacting dipoles, we reproduce the experimental measurements and predict that endogenous EF–mediated synchronizing effects should be relevant in the brain. Thus, experiments and models suggest that electric-dipole interactions contribute to synchronization of neighboring cortical columns.
Article of refrence:
Modulation of intercolumnar synchronization by endogenous electric fields in cerebral cortex. Beatriz Rebollo, Bartosz Telenczuk, Alvaro Navarro-Guzman, Alain Destexhe and Maria V. Sanchez-Vives Science Advances 03 Mar 2021: Vol. 7, no. 10, eabc7772 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abc7772